Views, Goals, and Filters can be set up to collect clean actionable data and measure target objectives.
Using filters can seem tricky or like a needless burden, but having clean data is essential in order to make the right decisions about your business marketing needs. Keeping the traffic data clean by adding filters within Google Analytics helps to keep the data from being skewed from internal traffic and spam-like “ghost traffic” from referral sources.
Filters in Analytics can be used to help improve the quality of traffic data in reports by allowing you to exclude data and include data. Google Analytics allows different types of filters, each type of filter offers customizable configuration options and each filter serves a direct purpose. Keep in mind that when traffic filter rules are applied, the filter rules will permanently filter traffic, which can not be recovered. Whereas segment filters will not permanently filter or change the traffic data.
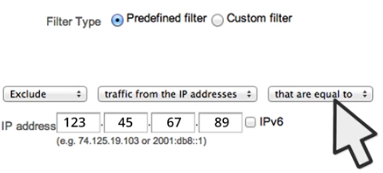
One of the most common filters that are set up in Google Analytics is a filter that will help to exclude internal company traffic.
Using an IP exclude filter helps to achieve this task.
Understanding traffic data will help provide a better idea of what is going on throughout your website, but how do you know if the website traffic data you are evaluating is clean? For example, if a page or section of the site is receiving a lot of traffic and if the average session duration is higher than other pages, this may indicate that the page has been found to be useful. If you are not sure where traffic to this page is coming from, then sorting this page traffic by Channels will give additional high-level insight. Click on Referral to view more information about traffic that has been referred from other websites. If you notice strange websites listed with multiple visits in a short period of time, the source of the traffic is most likely
"ghost referral traffic" or spam traffic. This type of traffic should be filtered out because it is not real traffic and it can drag down the good data that is reported. Filtering out this type of data from historical traffic data requires the use of
segments.
When creating filters in Google Analytics, start by creating different views, rather than just adding filters to the current view to protect the integrity of your data.
IMPORTANT: Before getting started with the process of setting up
reporting view filters, it is always best to rename the original traffic view to something like “Unfiltered View” before, creating a new View. Leaving the original view as the "Unfiltered View" will help to maintain the integrity of all of the original data.
To prevent possible data loss from a filter misconfiguration, typically it is recommended that filters should only be setup, monitored, and maintained by experienced Google Analytics users. Google Analytics will automatically create an unfiltered view when a new
property is added to the account, however, multiple
views are able to be set up with any property.
Once views and filters have been properly set up, you are ready to move onto creating Goals.
 Goals can help track and monitor business objectives:
Goals can help track and monitor business objectives: Special landing pages are often created in websites with a combination of the following elements: informational videos, infographics, links to reviews, social share or “Like” buttons, a submission form, and/or images with details about products and services.
Using Goals to track visitor interaction: The "right content" along with the types of elements noted above can help to direct visitors to complete an action, which can then be tracked as a goal. The most common example of this is completing an online purchase. Completing the purchase is tracked as the goal, and the revenue generated from the purchase helps to establish the value of the goal. However, goals are not just limited to eCommerce based websites.
About goals for non-eCommerce based websites
Setting up Goals to track within Google Analytics can help steer your business in the right direction: Adding goals within your Google Analytics account provides additional insight to website owners and marketing managers! Combining goals with the traffic data collected will allow you to gauge factors that are actually helping your website. This information can be captured in reports and analyzed, then used as part of the process when making decisions related to your online business marketing needs and requirements.
Many different types options are available when creating Goals for non-eCommerce based websites.
Types of Goals are available in Google Analytics:
- Pages per Sessions
- Destination
- Duration
- Event
Goals are able to provide data related to important visitor engagement metrics such as:
- Form submissions
- New account creations
- Newsletter signups
- Catalog downloads
- Any PDF downloads
The process of tracking events, accomplishments, and expectations is essential to help maintain a solid understanding of how your website is being used and interacted with by visitors, customers, and/or clients. Goals will help you do exactly that; gain an advantage by simplifying the process of tracking interactions within the site, rather than just visits to a page or section of the site.

Find out how our internet marketing and website development services can help your business grow online!